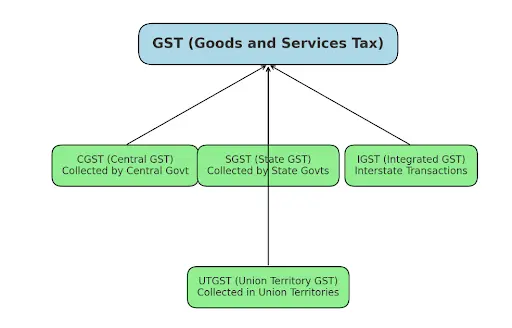
Types of GST in India - CGST, SGST, IGST, and UTGST


00:00 / 00:00
On July 1, 2017, India introduced a new indirect tax system called GST levied on the supply of Goods and Services. it is a unified indirect tax system that has replaced various taxes including VAT and service tax, thereby simplifying the tax structure. These taxes are collected from the final consumer of the goods and services and are paid to the respective authorities depending on the type of GST applicable. In this article, we will explore how many types of GST are there, the Difference between gst types, and how they work.
Types of GST Transactions
The GST is categorized based on the type of transaction on which the taxes are imposed to ensure equal tax distribution for both central and state governments. Primarily, GST considers two types of transactions: interstate and intra-state.
Inter-state transaction: The transaction that occurs due to the supply of goods and services between 2 states is called inter-state transaction.
Intra-state transaction: The transactions that occur due to the exchange of goods and services within one state are referred to as intra-state transactions.
Hence, by distinguishing between interstate and intrastate transactions, we can ascertain the applicable type of GST, whether it's CGST (Central Goods and Services Tax), SGST (State Goods and Services Tax), IGST (Integrated Goods and Services Tax), or UTGST (Union Territory Goods and Services Tax).
Types of GST Tax
Now that we understand the type of transactions considered while imposing GST, further, we’ll look into the components of GST in India.
Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST)
Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST)
State Goods and Services Tax (SGST)
Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST)
What is CGST?
Central Goods and Services Tax is a component of the GST regime governed by the provisions of the CGST Act. It is imposed by the central government on the supply of goods and services within the state. The revenue earned by CGST will go to the central government.
How does CGST Work?
If the selling price of the good is Rs.3,000 and the GST rate is 18%, then the amount chargeable to the buyer, including tax, will be Rs.3,540.
Here, if a seller sells goods worth Rs.3,000 to a buyer in the same state, then this 18% GST would be split equally between CGST and SGST. Out of the Rs.540, Rs.270 would consists of CGST, and Rs.270 would consist of SGST.
Here, the central government will get Rs.270 in the form of CGST, and the state government will get Rs.270 as SGST.
What is SGST?
State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) is another component of the GST regime. This is imposed by the state government on the supply of goods and services that take place within the same state, known as intra-state transactions. Here, the benefitting and regulating authority would be the state government.
How does SGST Work?
As mentioned in the above earlier example. If a trader sells goods worth Rs.3,000 to a customer within the same state and the GST is 18% which amounts to RS.540, the tax amount will be divided partly into CGST and SGST as 9% for both.
In this case, the tax amount of Rs.540 is divided into 2 amounting to Rs.270 each.
This Rs.270 will go to the state government in the form of SGST
What is IGST?
IGST or Integrated Goods and Services Tax is another component of the GST regime, it is levied by the central government on interstate supply (between 2 states) of goods and services. Governed by the IGST Act, the central government is responsible for collecting the tax. The collected IGST will then be distributed to central and state governments where the goods are consumed.
How does IGST Work?
For instance, if a seller from Tamilnadu sells goods worth Rs.2000 to a Buyer from Karnataka, the applicable GST rate is 18%, and the total GST on this amount would be Rs.360 which will entirely go to the central government.Further this portion is distributed among the Karnataka State government and central Government.
What is UTGST?
UTGST abbreviated to Union Territory Goods and Service Tax is a counterpart of SGST. Governed by the UTGST Act, it is imposed by the union territory government for the supply of goods and services that take place within the union territories. The union territories include the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Daman Diu, Dadra, Nagar Haveli, and Lakshadweep.
The tax revenue generated will be regulated and received by the union territory. It is a replacement for SGST in union territories and is levied alongside CGST.
How does UTGST Work?
Similar to intra-state, out of the overall GST collected, half will go to union territories and another half will go to the central government similar to the previous example given for the SGST.
Check out our latest blogs, "Tax Saving Investment Options" and "How to Save Tax in India" to learn more about tax-saving strategies and taxation in India!
Difference Between the Types of GST in India
Particulars | CGST | SGST | IGST | UTGST |
Regulatory Authority | Central Government | State Government | Central Government | Union Territory Government |
Benefitted Authority | Central Government | State Government | Central Government and Government of consuming state /UT | Union Territory Government |
Priority of Tax Credit | CGST, IGST | SGST, IGST | IGST, CGST, SGST | UTGST, IGST |
Applicability | Applicable for intra-state transactions(Within the same state) | Applicable for Intrastate transactions | Applicable for Interstate supplies | Applicable for transactions within union territory. |
Collection Process for Different GST Types
Final GST is collected from the end consumer of the goods and services. But, the product will be sold numerous times in between until it reaches the end consumer. Thus, in each activity of selling that product, the GST is collected from the buyer and paid by the seller to the authorities. Later, the collected tax amount is segregated based on the type of transaction (Interstate or intra state) such as CGST, SGST, IGST, and UTGST.
The segregated tax will then be distributed to central, state, or Union territory governments depending on the type GST applied.
Impact of Different GST Types on Businesses and Consumers
The different kinds of GST make it even easier for businesses and consumers to pay their taxes as it merges many taxes into one system. For example, a business would account for its sales in a state or union territory with CGST and SGST/UTGST but would be taxed with IGST on inter-state sales - thus simplifying compliance.
For the consumer, one of the key advantages of GST is clearer pricing because a single tax system tends to replace multiple systems of several taxes and sometimes makes goods and services cheaper to many. Again, this will vary with tax rate applied to certain goods.
Taxes Replaced by GST
The implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) replaced several taxes of both the state and the center. The levees that were replaced are listed below:
Taxes Replaced by GST (Central) | Taxes Replaced by GST (State) |
|
|
Read our latest articles, "RCM in GST", “Advantages of GST” and "IGST Full Form" to learn more about GST in India!
Conclusion
India's GST has streamlined taxation by consolidating several indirect taxes under a single uniform system. The four major types of this tax are- CGST, SGST, IGST, and UTGST. These are perceived to take care of the proportional transfer of revenues between the state and the central government by intra-state as well as inter-state transactions. This new tax regime makes doing business easier and ensures that the tax department is transparent and beneficial for both consumers and businesses.
For all your professional stock and investment decisions, visit Rupeezy, your more than able stockbroker partner, for hassle-free trades.
The content on this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. While we strive for accuracy, some information may contain errors or delays in updates.
Mentions of stocks or investment products are solely for informational purposes and do not constitute recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research before making any decisions.
Investing in financial markets are subject to market risks, and past performance does not guarantee future results. It is advisable to consult a qualified financial professional, review official documents, and verify information independently before making investment decisions.

All Category