Standard Deviation in Mutual Funds - Formula and Calculation


00:00 / 00:00
When investment analysts want to realize the risk inherent in a mutual fund, they often start by looking at what a measure of distribution is, usually the standard deviation in mutual fund performance. It helps to determine the variations of the data points from the mean value in a particular data set.
In finance, the standard deviation in mutual funds is essential in determining the degree of variability in investors’ returns. As there are many statistical purposes, this is also one of the most important in economics, accounting, and finance. The mutual funds’ standard deviation of annual returns in the portfolio shows how consistent the returns have been over the given period.
If a fund can make stable returns over time, the mutual fund standard deviation is likely to be low. Conversely, casually, a growth-oriented or emerging market fund goes through more up-and-down cycles, leading to a higher mutual fund standard deviation and is more risky. Let us help you better understand the standard deviation meaning in mutual funds so that you can understand risk.
What is Standard Deviation in Mutual Funds?
A mutual fund standard deviation is a percentage that shows how much a fund's returns might vary from its average annual return. Analyzing the benchmark returns will measure the fund’s variability when calculating the standard deviation of mutual fund returns over periods. The greater the fluctuation in value, the higher the coefficient of variation and, therefore, the more volatile the fund is.
Still, standard deviation results depend on averages, which are not considered good or bad. But that all depends on what you want to compare them with. For instance, assuming the standard deviation in mutual funds is 3, it can only be compared with a standard deviation of 2 or 4.
Use mutual fund standard deviation to match your risk level and investment goals when selecting a fund. If Fund A has more risk than Fund B, you should choose based on which one aligns with your risk tolerance.
Importance of Standard Deviation in Mutual Funds
When you're evaluating mutual funds, have you ever wondered how to gauge the risk level of your investment? That is why standard deviation in mutual funds is one of the main tools for this. But what is this phenomenon, and why should one pay attention to it?
Are you more comfortable with having an average return all year long, or are you okay with fluctuations in your returns? The standard deviation of mutual fund performance is where all this comes into play. This indicates that the returns will be volatile; therefore, the higher the standard deviation, the more oscillation, which could be satisfying or stressful depending on the investor.
Think of it this way: Which would you prefer for investment, a fund that increases by small percentages year in and year out or a fund that sometimes may increase by big percentages but also decrease by equally big percentages? From the standard deviation of a mutual fund, you can see the risk level of a fund. What do you agree or disagree with is it desirable to take risks in the hope of a greater reward? Or do you like regularity, that is, constancy of the conditions that dictate the conduct of your life?
To know about the long-term and short-term goals, it is imperative to understand the standard deviation in mutual funds. It’s one of the best tools to assess whether a fund’s risk is aligned with your goals and comfort level.
How Standard Deviation Measures Volatility?
When it comes to investing, understanding the volatility of your mutual fund can help you make informed decisions. Standard deviation is the go-to metric for this it measures how much the returns of a mutual fund fluctuate compared to its average return.
Standard Deviation Calculation
Let’s break it down with a simple formula and example.
The standard deviation formula in mutual funds looks like this:
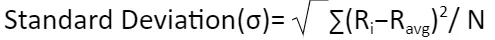
Ri = Each return in the dataset
Ravg = Average return
N= Number of observations
In simpler terms, it’s a measure of how much the returns deviate from the average return over a period.
Example: Calculating Standard Deviation in Mutual Funds
Let’s say you invested in a mutual fund for five years, and the annual returns were:
Year 1: 10%
Year 2: 12%
Year 3: 9%
Year 4: 13%
Year 5: 11%
To calculate the standard deviation in mutual funds, follow these steps:
1) Find the Average Return:
Ravg = (10+12+9+13+11)/5 = 11%
2) Calculate the Variance for Each Year:
Variance of year 1 = (10-11)^2=1
Variance of year 2 = (12-11)^2=1
Variance of year 3 = (9-11)^2=4
Variance of year 4 = (13-11)^2=4
Variance of year 5 = (11-11)^2=0
3) Sum the Variances:
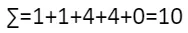
10/5=2
5) Take the Square Root to Find the Standard Deviation:
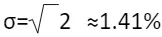
Read our latest blogs “Rolling Returns of Mutual Funds”, “Open Ended Mutual Funds” and “Mutual Fund Distributor Commission” to learn more about mutual funds!
Low vs High Standard Deviation
A low standard deviation indicates that a mutual fund’s returns are relatively stable and close to the average. This means fewer ups and downs in performance. If you have a lower risk tolerance or are nearing retirement, low standard deviation funds may offer the stability you need.
A high standard deviation means the fund’s returns are more spread out from the average, showing greater volatility. This can lead to higher potential gains but also greater losses. For aggressive investors willing to take on more risk, high standard deviation funds can offer the potential for higher returns.
How Standard Deviation in Mutual Fund Helps Investors
Risk Assessment: Knowing whether a fund has a low or high standard deviation helps you assess whether it fits your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Investment Strategy: It aids in selecting investments that align with your overall strategy, whether you're looking for stability or are willing to accept higher risk for potential rewards.
Performance Expectation: Understanding the standard deviation allows you to set realistic expectations for the potential volatility of your investment and plan accordingly.
Diversification Decisions: By evaluating standard deviation, you can better diversify your portfolio to balance stable and volatile assets.
Pros and Cons of Standard Deviation in Mutual Funds
Pros
Measures Volatility: Standard deviation helps investors understand the potential fluctuations in a mutual fund's returns, making it easier to assess volatility.
Risk Indicator: It provides a clear indicator of the risk associated with a fund, allowing you to align your investments with your risk tolerance.
Easy Comparison: Investors can compare the standard deviation of different funds to choose one that matches their risk profile.
Historical Data Insight: By analyzing past performance, standard deviation gives a historical view of how much returns have varied.
Objective Measurement: It is a mathematical, unbiased measure of risk, offering a consistent method to evaluate different funds.
Cons
Based on Past Performance: It relies on historical data, which may not accurately predict future performance or risk.
Doesn't Account for Market Changes: Standard deviation doesn't factor in potential market shifts, economic changes, or unforeseen events.
Doesn’t Measure Potential Gains: It only shows how much returns deviate from the average, not the potential for high returns.
May Mislead in Stable Markets: During stable market periods, a low standard deviation might give a false impression that a fund is low risk, even if it has inherent volatility.
Doesn’t Include Other Risks: Other essential factors like liquidity risk or credit risk are not captured by standard deviation alone.
Comparing Standard Deviation
It assists you to compare the level of risk of a fund with its peer group and benchmark or index. It shows whether a fund’s movements are bigger or smaller than other’s movements.
Let’s look at two large-cap funds to understand how their standard deviation compares with the average for the category and the benchmark: Let’s look at two large-cap funds to understand how their standard deviation compares with the average for the category and the benchmark:
Fund Name | Standard Deviation of the Fund | Average Standard Deviation of the Category | Standard Deviation of the Benchmark |
Aditya Birla Sun Life Frontline Equity | 14.25 | 12.37 | 22.20 |
Nippon India Large Cap | 25.22 | 22.47 | 22.20 |
You find that while the first mutual fund we discussed is closer to the category average and the benchmark we looked at earlier, the second mutual fund has a higher standard deviation, which signifies higher volatility. This doesn’t mean that the higher standard deviation of Nippon India's Large Cap is necessarily a disadvantage. Instead, as an investor, you should consider how each fund fits your return expectations and risk tolerance before deciding.
How Standard Deviation Works in Measuring Risks in Mutual Funds
In simple terms, the standard deviation in mutual funds is a statistical measure that shows how much a fund’s returns can vary from its average. It helps answer the question: How many fluctuations of returns could there be from the expected return?
If a mutual fund has a high standard deviation, its returns fluctuate widely, which means more risk.
A low standard deviation suggests more consistent returns, making the fund less volatile.
The risk in mutual funds is the uncertainty in the returns. By using standard deviation, you get a clearer picture of how risky a fund is:
Low standard deviation: Generally, it is preferred to have a fund for which the return rate will not be as volatile and, thus, will be safer. For instance, most debt or balanced funds are bound to portray low standard deviation figures due to investments with relatively low risks or low variance.
High standard deviation: An ever-fluctuating fund has a greater risk because its returns fluctuate more widely than a consistent and stable fund. For instance, the standard deviation of funds invested in emerging markets or growth stocks is normally high because the investments are unpredictable.
Standard deviation is useful not only in identifying risk but also in managing it. When choosing a fund, you can compare the standard deviation of different funds within the same category. For example:
If the two equity funds have different standard deviations, then the one with the greater SD is said to be riskier, and in turn, it will, in most cases, have higher returns but with more risk in comparison to the lower SD of equity fund.
What is a good standard deviation in mutual funds? This will depend on your appetite to lose your capital investment. The investor must invest in funds with lower standard deviation for lower risk. If one is willing to accept the volatility of the markets then he might prefer funds with a higher SD.
Tips for Investors to Use Standard Deviation and Managing Risk
Understanding standard deviation is key to managing risk effectively when investing in mutual funds. Standard deviation in mutual funds tells you how much the fund's returns fluctuate from its average. Here are some practical tips on using SD to manage risk in your portfolio.
Know Your Risk Appetite
Compare Funds Within the Same Category
Use SD to Assess Portfolio Stability
Understand That Higher SD Equals Higher Risk
Monitor SD Over Time
Consider Standard Deviation Alongside Other Metrics
Use SD to Set Investment Expectations
Check out our latest articles “Types of Mutual Funds”, “IDCW in Mutual Fund” and “What is XIRR in Mutual Fund” to learn more about mutual funds!
Conclusion
Standard deviation is an important measure that helps rank mutual funds concerning risk and return. By measuring how much a fund’s returns deviate from its average, standard deviation helps investors gauge the consistency and reliability of a fund's performance. A lower standard deviation in mutual funds indicates more stable returns, while a higher standard deviation points to greater variability and potential risk.
For those who want to track their investments more effectively and get access to many different mutual funds, the Rupeezy website is suitable. Rupeezy is India’s cheapest discount stock broker that provides customers with some of the best rates and great trading platforms that can assist investors in making the right choices and making the best investments. Begin managing your investments with Rupeezy right away.
The content on this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. While we strive for accuracy, some information may contain errors or delays in updates.
Mentions of stocks or investment products are solely for informational purposes and do not constitute recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research before making any decisions.
Investing in financial markets are subject to market risks, and past performance does not guarantee future results. It is advisable to consult a qualified financial professional, review official documents, and verify information independently before making investment decisions.

All Category









