What Is Solvency Ratio?


00:00 / 00:00
When you plan to invest in a company, what things do you consider? Well, this is one of the most common questions that you will come across when trading and investing. Where many people focus on checking the past year's performance, others might look into the plans. But there is one thing that you must actually check. These are the key financial ratios.
These include some simple ratios like current ratio or quick ratio, to complex ones like ROCE, ROE, and other profitability ratios. One such ratio is the solvency ratio that highlights the company’s ability to manage long-term liabilities.
But why should you check the solvency ratio, and what exactly is it all about? If you are also looking for an answer, then read this guide to know more.
What Is Solvency Ratio?
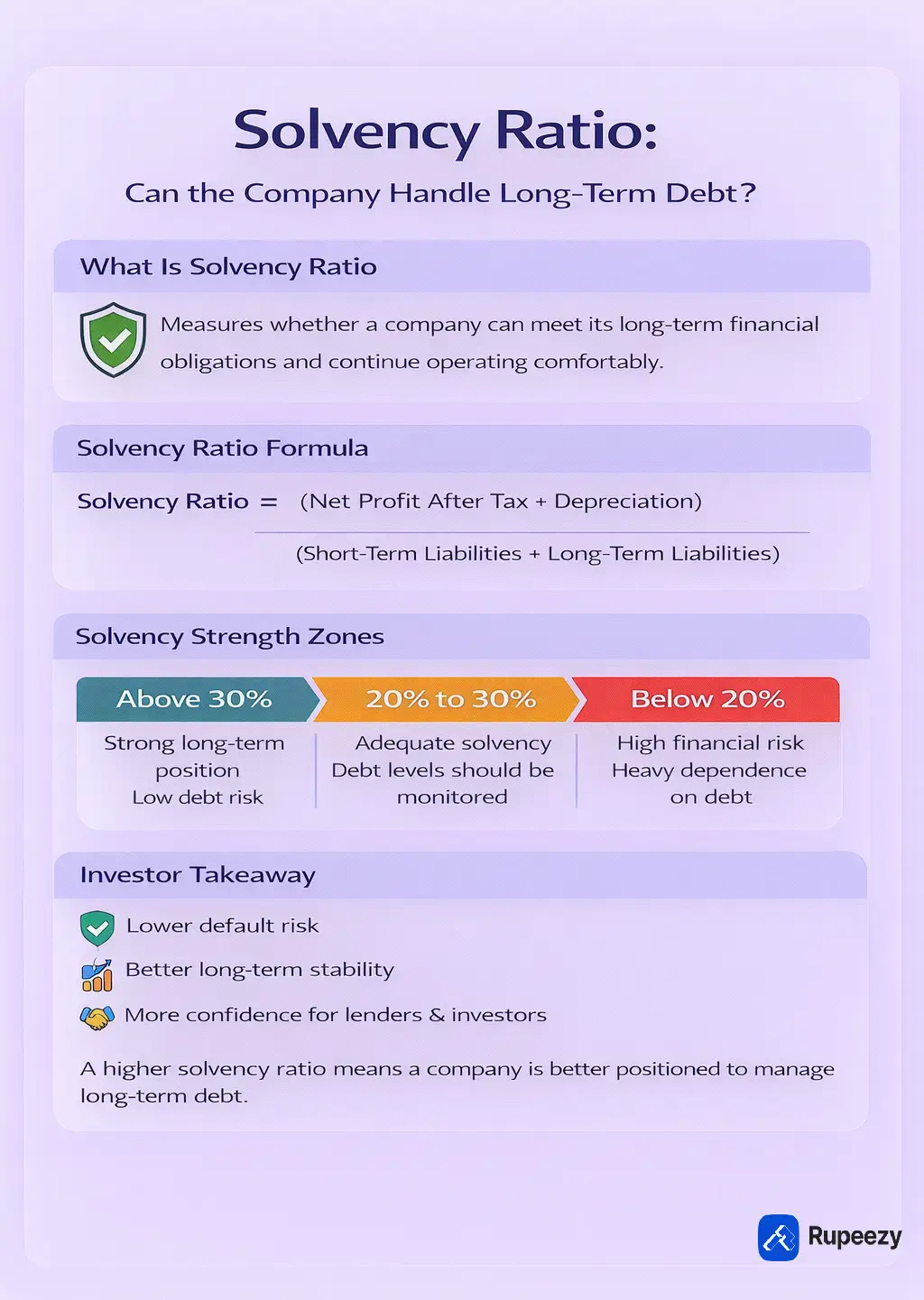
The solvency ratio is a financial ratio. It measures a company’s ability to meet its long-term financial obligations. It helps you to understand the condition of the company in terms of earnings and assets. A good amount shows that the company is in a position to manage its debt and liabilities well.
Unlike short-term ratios, the solvency ratio focuses on long-term financial stability. This is a ratio that talks about the overall business sustainability.
In simple terms, the solvency ratio shows whether a company can continue operating without facing long-term debt pressure. A higher solvency ratio indicates stronger financial health, while a lower ratio suggests higher financial risk.
Key Features of Solvency Ratio
The solvency ratio highlights a company’s long-term financial position. It focuses on stability and risk. The idea here is not to analyse the short-term cash flow. When you use this ratio, you can show your lenders that the money is generating returns for them. Some of the key features of the solvency ratio that you should know are as follows:
Measures the ability to repay long-term liabilities.
Focuses on overall financial stability.
Considers profits and non-cash expenses like depreciation.
Helps assess long-term business sustainability.
Useful for investors, lenders, and analysts.
Indicates the level of financial risk in a company.
Solvency Ratio Formula Explained
The solvency ratio shows how well a company can cover its total debts using its earnings and asset strength. It focuses on long-term financial health and helps understand whether the business can meet its obligations without financial stress.
In simple terms, the solvency ratio looks at two key things:
Profit earned by the company, which is the net profit after tax
Value of assets after adjusting for depreciation, which reflects real earning capacity
Solvency Ratio Formula
Solvency Ratio = (Net Profit After Tax + Depreciation) ÷ (Short-Term Liabilities + Long-Term Liabilities)
This formula compares what the company earns with what it owes.
Example of Solvency Ratio
Let us assume that there is a company A with the following details.
Net profit after tax: Rs. 30 lakh
Depreciation: Rs. 20 lakh
Short-term liabilities: Rs. 1 crore
Long-term liabilities: Rs. 1.5 crore
Total liabilities = Rs. 2.5 crore
Solvency Ratio = (30 + 20) ÷ 250 = 0.20 or 20%
A solvency ratio of 20% indicates that the company is reasonably capable of meeting its total debt obligations over time.
Interpretation of Solvency Ratio
The solvency ratio becomes meaningful only when it is interpreted correctly. When you do so, you are in a better position to analyse the condition of the company and make an informed investment call.
Category | General Percentage Range | Interpretation |
High | Above 30% | Strong long-term financial position with low debt risk |
Moderate | 20% to 30% | Adequate ability to meet long-term liabilities |
Low | Below 20% | Higher dependence on debt and increased financial risk |
Types of Solvency Ratios
To better assess a company’s ability to meet its long-term debt obligations, solvency ratios are divided into different types. Each ratio is used for a special purpose. But the ultimate aim is to see how well the funds are used for long-term stability. So, the key ratios that are used are as follows:
1. Debt-to-Equity Ratio
This is the ratio that considers the long-term debt and the shareholders’ equity. It measures the amount of debt that the company is using against equity. It helps know the balance between borrowed funds and owners’ funds.
Formula: Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Long-Term Debt ÷ Shareholders’ Equity
Interpretation
If the ratio is high, then the company is mostly using debt, which is not good. This increases the overall financial risk.
If the ratio is low, then it means the company is using equity more. This is a sign of safety and stability, which makes a company good for investment.
2. Debt Ratio
The debt ratio evaluates the proportion of a company’s assets that are financed through total liabilities. It gives a broad view of overall leverage.
Formula: Debt Ratio = Total Liabilities ÷ Total Assets
Interpretation:
If you find that this ratio is high, then the amount of liability is higher. This means you do not have sufficient assets to pay off debts. This is risky and shows inefficient management.
If the ratio is low, then it means the company is investing more in assets. This means the company has a sufficient amount of assets to pay the debt when needed. This shows slow dependence on borrowings and safety.
3. Proprietary Ratio or Equity Ratio
The proprietary ratio, also known as the equity ratio, measures the share of shareholders’ equity in total assets. It reflects how well assets are backed by owners’ funds.
Formula: Proprietary Ratio = Shareholders’ Equity ÷ Total Assets
Interpretation:
A higher proprietary ratio indicates strong long-term solvency and financial stability. It shows that the company relies more on equity rather than debt for asset financing.
When the same ratio is low, there is a question about financial stability. The amount of equity that a company should use is missing, which makes the business unstable.
4. Interest Coverage Ratio
The interest coverage ratio shows how easily a company can pay interest on its outstanding debt using operating profits.
Formula: Interest Coverage Ratio = EBIT ÷ Interest Expense
Interpretation:
A higher ratio means the company can comfortably meet its interest obligations. This means the company has sufficient surplus and is in good standing.
A lower ratio indicates potential difficulty in servicing debt and higher financial stress. This is a sign that the company's standing is not good in the market.
Pros and Cons of Solvency Ratios
Solvency ratios are widely used to judge a company’s long-term financial health. But unlike any other analysis, there are pros and cons to using the same.
Pros
Helps assess the long-term financial stability of a company.
Useful for investors to evaluate business risk before investing.
Assists lenders in judging loan repayment capacity.
Shows the level of dependence on debt financing.
Supports comparison of companies within the same industry.
Cons
Not good for short-term position analysis.
Vary for all sectors and industries.
Based on accounting data, which may include estimates.
Does not consider future cash flows or growth plans.
May give a misleading picture if used alone without other ratios.
Conclusion
The solvency ratio plays a key role in understanding a company’s long-term financial strength. It helps the investors and the lenders to know about the status of the company well. But these alone are not enough. You need to do proper technical analysis as well.
And to do this, you would need access to the tools and guidance. This is where Rupeezy offers you all the details you need. Register and start investing right.
FAQs
What is a good solvency ratio?
A solvency ratio above 20% is generally considered healthy. But it will be different for every industry.
Why is the solvency ratio important for investors?
Investors use the solvency ratio to determine the stability and debt-asset management of the company.
How is the solvency ratio different from the liquidity ratio?
Solvency ratio focuses on long-term obligations, while liquidity ratio measures short-term repayment ability.
Can a company survive with a low solvency ratio?
A company can operate with a low solvency ratio, but it carries higher financial risk and may face problems during downturns.
Should the solvency ratio be used alone for analysis?
No, it should be used along with other financial ratios to get a complete view of a company’s financial health.
The content on this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. While we strive for accuracy, some information may contain errors or delays in updates.
Mentions of stocks or investment products are solely for informational purposes and do not constitute recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research before making any decisions.
Investing in financial markets are subject to market risks, and past performance does not guarantee future results. It is advisable to consult a qualified financial professional, review official documents, and verify information independently before making investment decisions.

All Category









