US CPI and Fed Rate: Understanding the Influence on US and Indian Markets


00:00 / 00:00
In April, the most anticipated data, the US inflation hit its lowest level in almost two years. The Consumer Price Index rose by 4.9% over the last year.
The CPI inflation rate cooled down from 9.1% in June 2022, an all time high level in 40 years! The drop was lower than what experts had estimated.
The drop was attributed to falling grocery prices even though gasoline, rentals and used car prices rose, though at a slower pace.
Experts point that overall prices have been increasing slower than before, with Covid related supply chain issues easing.
Core CPI which does not include food and energy and indicates trends rose by 0.4% from March and 5.5% from a year ago.
CPI inflation chart for the past 3 years:
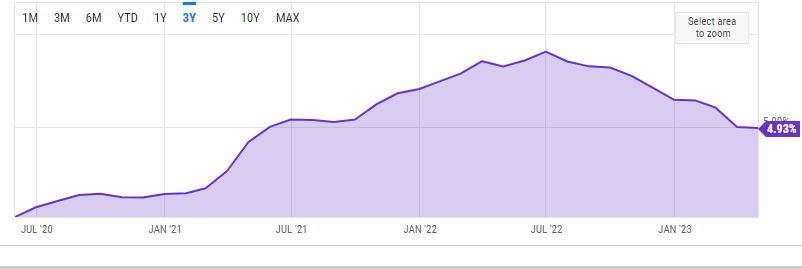
Source: YTCharts
Why is CPI important for the US economy?
To control the high inflationary pressure in the economy, FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) took aggressive steps and hiked interest rates ten times consecutively with a total hike of 5 percentage points since March 2022.
The interest rate is highest in over 15 years and steepest since 1980s. CPI is still not within Fed’s 2% long term target.
In the last FOMC meeting early MAy, Fed hiked the interest rates by 25 basis points and hinted it may pause rate hike in the upcoming June meeting.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell said, “it is now an open question whether further increases will be warranted in an economy still facing high inflation.
But also showing signs of a slowdown and with risks of a tough credit crackdown by banks on the horizon. We’re closer, or maybe even there,”
What is the impact of Fed rate hike?
When US Federal Reserve increases interest rates, the cost of borrowing goes up.
Interbank rates for short term loans go up and consumer loans become more expensive with soaring interest costs for retail as well as businesses.
This reduces demand for loans and spending, and higher interest rates drive consumers to save more, thus reducing money supply in the market. It limits the increase in price of goods.
How does CPI and Fed Interest Rate Policy impact Indian markets?
FIIs make up one of the largest chunk of investors in the Indian markets and their investing decisions impact the overall market direction and share prices.
When rates increase in U.S. markets, better yields witness flight of funds to U.S. assets from other markets.
The capital outflow weakens the domestic currency and prompts regulator to hike interest rates to curb the outflow and reduce the rate differential.
To control the falling domestic currency RBI sells USD from forex reserve to build demand. Higher domestic interest rates impact consumer and business loan offtake in near term, and impacts overall economic activity.
Investors globally are monitoring future monetary policy changes, US debt ceiling deadline looming ahead.
The situation is still evolving and it’s a tightrope walk for policymakers with the U.S. economy facing multiple challenges of inflation, recent bank failures and economic slowdown.
The content on this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. While we strive for accuracy, some information may contain errors or delays in updates.
Mentions of stocks or investment products are solely for informational purposes and do not constitute recommendations. Investors should conduct their own research before making any decisions.
Investing in financial markets are subject to market risks, and past performance does not guarantee future results. It is advisable to consult a qualified financial professional, review official documents, and verify information independently before making investment decisions.

All Category






